
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Novel Asian-Specific Visceral Adiposity Indices Are Associated with Chronic Kidney Disease in Korean Adults
- Jonghwa Jin, Hyein Woo, Youngeun Jang, Won-Ki Lee, Jung-Guk Kim, In-Kyu Lee, Keun-Gyu Park, Yeon-Kyung Choi
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(3):426-436. Published online March 6, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0099
- 2,476 View
- 128 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The Chinese visceral adiposity index (CVAI) and new visceral adiposity index (NVAI) are novel indices of visceral adiposity used to predict metabolic and cardiovascular diseases in Asian populations. However, the relationships of CVAI and NVAI with chronic kidney disease (CKD) have not been investigated. We aimed to characterize the relationships of CVAI and NVAI with the prevalence of CKD in Korean adults.
Methods
A total of 14,068 participants in the 7th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (6,182 men and 7,886 women) were included. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analyses were employed to compare the associations between indices of adiposity and CKD, and a logistic regression model was used to characterize the relationships of CVAI and NVAI with CKD prevalence.
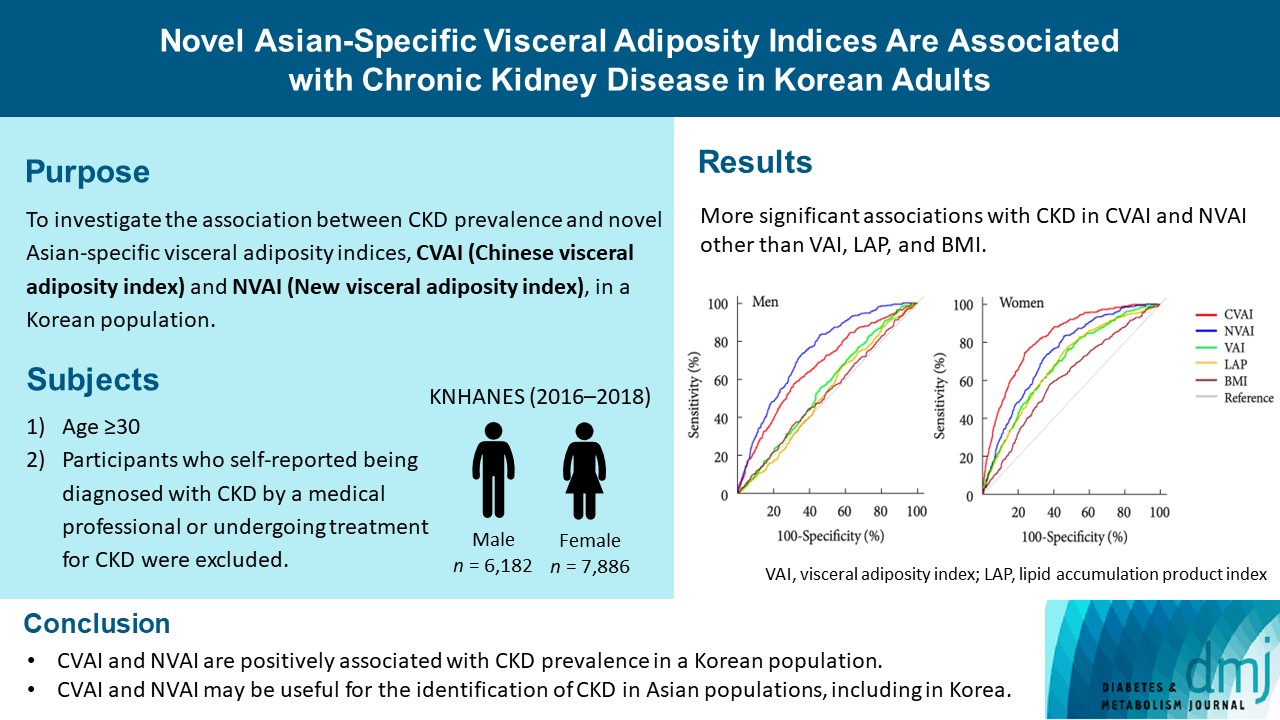
Results
The areas under the ROC curves for CVAI and NVAI were significantly larger than for the other indices, including the visceral adiposity index and lipid accumulation product, in both men and women (all P<0.001). In addition, high CVAI or NVAI was significantly associated with a high CKD prevalence in both men (odds ratio [OR], 2.14; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.31 to 3.48 in CVAI and OR, 6.47; 95% CI, 2.91 to 14.38 in NVAI, P<0.05) and women (OR, 4.87; 95% CI, 1.85 to 12.79 in CVAI and OR, 3.03; 95% CI, 1.35 to 6.82 in NVAI, P<0.05); this association remained significant after adjustment for multiple confounding factors in men and women.
Conclusion
CVAI and NVAI are positively associated with CKD prevalence in a Korean population. CVAI and NVAI may be useful for the identification of CKD in Asian populations, including in Korea. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between Chinese visceral adiposity index and risk of stroke incidence in middle-aged and elderly Chinese population: evidence from a large national cohort study
Zenglei Zhang, Lin Zhao, Yiting Lu, Xu Meng, Xianliang Zhou
Journal of Translational Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Association between Chinese visceral adiposity index and risk of stroke incidence in middle-aged and elderly Chinese population: evidence from a large national cohort study
- Drug/Regimen
- Evogliptin, a Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor, Attenuates Renal Fibrosis Caused by Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction in Mice
- Mi-Jin Kim, Na-young Kim, Yun-A Jung, Seunghyeong Lee, Gwon-Soo Jung, Jung-Guk Kim, In-Kyu Lee, Sungwoo Lee, Yeon-Kyung Choi, Keun-Gyu Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(1):186-192. Published online October 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0271
- 5,658 View
- 97 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Renal fibrosis is considered to be the final common outcome of chronic kidney disease. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors have demonstrated protective effects against diabetic kidney disease. However, the anti-fibrotic effect of evogliptin, a DPP-4 inhibitor, has not been studied. Here, we report the beneficial effects of evogliptin on unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO)-induced renal fibrosis in mice. Evogliptin attenuated UUO-induced renal atrophy and tubulointerstitial fibrosis. Immunohistochemistry and Western blotting demonstrated that evogliptin treatment inhibits pro-fibrotic gene expressions and extracellular matrix production.
In vitro findings showed that the beneficial effects of evogliptin on renal fibrosis are mediated by inhibition of the transforming growth factor-β/Smad3 signaling pathway. The present study demonstrates that evogliptin is protective against UUO-induced renal fibrosis, suggesting that its clinical applications could extend to the treatment of kidney disease of non-diabetic origin.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Targeting cluster of differentiation 26 / dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (CD26/DPP4) in organ fibrosis
Birte Ohm, Isabelle Moneke, Wolfgang Jungraithmayr
British Journal of Pharmacology.2023; 180(22): 2846. CrossRef - Linagliptin ameliorates pulmonary fibrosis in systemic sclerosis mouse model via inhibition of endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition
Biwei Pei, Na Zhang, Tingting Pang, Gengyun Sun
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry.2022; 477(4): 995. CrossRef - Association Between DPP4 Inhibitor Use and the Incidence of Cirrhosis, ESRD, and Some Cancers in Patients With Diabetes
Yewon Na, Soo Wan Kim, Ie Byung Park, Soo Jung Choi, Seungyoon Nam, Jaehun Jung, Dae Ho Lee
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 107(11): 3022. CrossRef - Evogliptin Directly Inhibits Inflammatory and Fibrotic Signaling in Isolated Liver Cells
Hye-Young Seo, So-Hee Lee, Eugene Han, Jae Seok Hwang, Sol Han, Mi Kyung Kim, Byoung Kuk Jang
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(19): 11636. CrossRef - Optimization and validation of a fluorogenic dipeptidyl peptidase 4 enzymatic assay in human plasma
Hyunyee Yoon, Su Hee Cho, Yu Rim Seo, Kyung-Sang Yu, Sung Sup Park, Moon Jung Song
Analytical Biochemistry.2021; 612: 113952. CrossRef - Use of Anti-Diabetic Agents in Non-Diabetic Kidney Disease: From Bench to Bedside
Sungjin Chung, Gheun-Ho Kim
Life.2021; 11(5): 389. CrossRef - Targeting Dermal Fibroblast Subtypes in Antifibrotic Therapy: Surface Marker as a Cellular Identity or a Functional Entity?
Xin Huang, Yimin Khoong, Chengyao Han, Dai Su, Hao Ma, Shuchen Gu, Qingfeng Li, Tao Zan
Frontiers in Physiology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of evogliptin treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes: A multicentre, active‐controlled, randomized, double‐blind study with open‐label extension (the EVERGREEN study)
Gyuri Kim, Soo Lim, Hyuk‐Sang Kwon, Ie B. Park, Kyu J. Ahn, Cheol‐Young Park, Su K. Kwon, Hye S. Kim, Seok W. Park, Sin G. Kim, Min K. Moon, Eun S. Kim, Choon H. Chung, Kang S. Park, Mikyung Kim, Dong J. Chung, Chang B. Lee, Tae H. Kim, Moon‐Kyu Lee
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2020; 22(9): 1527. CrossRef Effect of Switching from Linagliptin to Teneligliptin Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors in Older Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Eugene Han, Minyoung Lee, Yong-ho Lee, Hye Soon Kim, Byung-wan Lee, Bong-Soo Cha, Eun Seok Kang
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2020; Volume 13: 4113. CrossRef- Efficacy and safety of novel dipeptidyl-peptidase-4 inhibitor evogliptin in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis
Deep Dutta, Saptarshi Bhattacharya, Aishwarya Krishnamurthy, LokeshKumar Sharma, Meha Sharma
Indian Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 24(5): 434. CrossRef
- Targeting cluster of differentiation 26 / dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (CD26/DPP4) in organ fibrosis
- Prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus and Prediabetes in Dalseong-gun, Daegu City, Korea
- Jung-Eun Lee, Sung-Chang Jung, Gui-Hwa Jung, Sung-Woo Ha, Bo-Wan Kim, Shung-Chull Chae, Wee-Hyun Park, Ji-Sun Lim, Jin-Hoon Yang, Sin Kam, Byung-Yeol Chun, Jong-Yeon Kim, Jung-Jeung Lee, Kyeong-Soo Lee, Moon-Young Ahn, Young-Ae Kim, Jung-Guk Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2011;35(3):255-263. Published online June 30, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2011.35.3.255
- 4,854 View
- 37 Download
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background The aim of the present study was to determine the population-based prevalence of diabetes mellitus (DM) and prediabetes in a rural district of Daegu City, Korea.
Methods Between August and November 2003, a community-based health survey of adults aged 20 years and older was performed in the rural district of Dalseong-gun in Daegu City. A total of 1,806 of all eligible individuals agreed to participate. Fasting plasma glucose was measured in all participants. Two hour oral glucose tolerance was measured in the 1,773 participants for whom there was neither an established diagnosis of DM nor evidence of DM according to fasting glucose levels. The prevalence of DM and prediabetes was determined according to the 2003 criteria of the American Diabetes Association. Subjects with prediabetes were classified into one of three categories of glucose intolerance: isolated impaired fasting glucose (IFG); isolated impaired glucose tolerance (IGT); or combined IFG and IGT.
Results The prevalence of DM was 12.2%. The highest prevalence rates were observed in subjects in their seventies. A total of 34.7% of all subjects who were assigned a diagnosis of DM in the present study had not been diagnosed previously. The prevalence of prediabetes was 22.7%. The highest prevalence rates were observed in subjects in their fifties.
Conclusion The present study identified prevalence rates of 12.2% for DM (age-standardized prevalence rate [ASR], 6.8%), and 22.7% for prediabetes (ASR 18.5%). These results emphasize the need for community health promotion strategies to prevent or delay the onset of DM in individuals with prediabetes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Rural-urban differentials of prevalence and lifestyle determinants of pre-diabetes and diabetes among the elderly in southwest China
Yi Zhao, Hui-fang Li, Xia Wu, Guo-hui Li, Allison Rabkin Golden, Le Cai
BMC Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Prevalence of Diabetes, Prediabetes and Associated Risk Factors in Hangzhou, Zhejiang Province: A Community-Based Cross-Sectional Study
Mingming Shi, Xiao Zhang, Hui Wang
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2022; Volume 15: 713. CrossRef - Epidemiology of Isolated Impaired Glucose Tolerance Among Adults Aged Above 50 Years in Rural China
Xiaobing Tian, Yan Li, Jie Liu, Qiuxing Lin, Qiaoxia Yang, Jun Tu, Jinghua Wang, Jidong Li, Xianjia Ning
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2021; Volume 14: 4067. CrossRef - Association between Frequency of Breakfast Consumption and Insulin Resistance Using Triglyceride-Glucose Index: A Cross-Sectional Study of the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2016–2018)
Hye Jin Joo, Gyu Ri Kim, Eun-Cheol Park, Sung-In Jang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(9): 3322. CrossRef - The prevalence of prediabetes and associated conditions in Ahmedabad population
Bhoomi Arora, Snehal S. Patel, Banshi D. Saboo
International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries.2020; 40(1): 61. CrossRef - STUDY OF DYSLIPIDAEMIA AMONG PRE-DIABETIC PATIENTS
Ravikumar Ravikumar, Gopal Krishnamurthy S. N, Anil Kumar T., Ashwin Kulkarni, Bhavanashree Magaji, Gayatri Sujive
Journal of Evidence Based Medicine and Healthcare.2019; 6(36): 2480. CrossRef - Prevalence of Pre-Diabetes across Ethnicities: A Review of Impaired Fasting Glucose (IFG) and Impaired Glucose Tolerance (IGT) for Classification of Dysglycaemia
Wilson Yip, Ivana Sequeira, Lindsay Plank, Sally Poppitt
Nutrients.2017; 9(11): 1273. CrossRef - Epidemiology of abnormal glucose metabolism in a country facing its epidemic: SAUDI‐DM study
Khalid Al‐Rubeaan, Hamad A. Al‐Manaa, Tawfik A. Khoja, Najlaa A. Ahmad, Ahmad H. Al‐Sharqawi, Khalid Siddiqui, Dehkra Alnaqeb, Khaled H. Aburisheh, Amira M. Youssef, Abdullah Al‐Batel, Metib S. Alotaibi, Ali A. Al‐Gamdi
Journal of Diabetes.2015; 7(5): 622. CrossRef - Association of Adiposity Trajectories With Insulin Sensitivity and Glycemic Deterioration
Rong Liu, Wendy J. Brickman, Katherine K. Christoffel, Xin Liu, Guoying Wang, Lester Arguelles, Shanchun Zhang, Donald Zimmerman, Binyan Wang, Xiping Xu, Zhiping Li, Houxun Xing, Xiaobin Wang
Diabetes Care.2012; 35(7): 1506. CrossRef
- Rural-urban differentials of prevalence and lifestyle determinants of pre-diabetes and diabetes among the elderly in southwest China
- Factors that Affect Medication Adherence in Elderly Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
- Kyung-Ae Park, Jung-Guk Kim, Bo-Wan Kim, Sin Kam, Keon-Yeop Kim, Sung-Woo Ha, Sung-Taek Hyun
- Korean Diabetes J. 2010;34(1):55-65. Published online February 28, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2010.34.1.55
- 4,487 View
- 96 Download
- 35 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background This study was conducted to evaluate the factors affecting medication adherence in geriatric diabetic patients treated at private clinics and tertiary hospitals. We compared the factors affecting medication adherence between these two patient groups.
Methods We included 108 diabetic patients older than 65 years treated at one tertiary hospital and 157 patients older than 65 years treated at two private clinics. We conducted an interview survey based on the Health Belief Model, and used a questionnaire that included the self-efficacy variable. For the medication adherence, Morisky's self-report was used.
Results The medication adherence based on Morisky's self-report was significantly higher in tertiary hospital patients (61.1%) compared to private clinic patients (43.2%) (
P < 0.01). The results showed that drug storage and self-efficacy were factors affecting adherence to medication in tertiary hospital patients (P < 0.05). The adherence was high in cases of proper drug storage (odds ratio [OR], 5.401) and in cases with high self-efficacy (OR, 13.114). In private clinic patients, financial level (P < 0.05), recognition of the seriousness of diabetes complications (P < 0.05) and self-efficacy (P < 0.01) were associated with medication adherence. The medication adherence was significantly lower in patients whose financial state were moderate than those with lower (OR, 0.410), and medication adherence was significantly higher in patients who had higher perceived severity (OR, 2.936) and in patients with higher self-efficacy (OR, 4.040).Conclusion Different strategies should be used to increase medication adherence in geriatric diabetic patients, depending on institutions whether they are treated.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Medication use problems among older adults at a primary care: A narrative of literature review
Christina Christopher, Bhuvan KC, Sunil Shrestha, Ali Qais Blebil, Deepa Alex, Mohamed Izham Mohamed Ibrahim, Norhasimah Ismail
AGING MEDICINE.2022; 5(2): 126. CrossRef - Changes in Treatment Satisfaction Over 3 Years in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes After Initiating Second-line Treatment
Tomoya Mita, Naoto Katakami, Mitsuyoshi Takahara, Masaru Kawashima, Fumitaka Wada, Hiroki Akiyama, Naru Morita, Yoko Kidani, Toshitaka Yajima, Iichiro Shimomura, Hirotaka Watada
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 107(9): 2424. CrossRef - Associated factors with treatment adherence of patients diagnosed with chronic disease: Relationship with health literacy
Sabahat Coskun, Gulcan Bagcivan
Applied Nursing Research.2021; 57: 151368. CrossRef - The relationships among self-efficacy, health literacy, self-care and glycemic control in older people with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Ariyanti Saleh, Wirda Wirda, Andi Masyitha Irwan, Aulia Insani Latif
Working with Older People.2021; 25(2): 164. CrossRef - Tip 2 Diyabetli Bireylerin Hastalık Yönetiminde Karşılaştıkları Engellerin Değerlendirilmesi
Şuheda ÜSTÜNDAĞ, Nuray DAYAPOĞLU
Adnan Menderes Üniversitesi Sağlık Bilimleri Fakültesi Dergisi.2021; 5(3): 514. CrossRef - Influence of Health Literacy on Medication Adherence Among Elderly Females With Type 2 Diabetes in Pakistan
Nadia Hussain, Amira S. A. Said, Zainab Khan
International Quarterly of Community Health Education.2020; 41(1): 35. CrossRef - Elucidating factors associated with non-adherence among Type 1 diabetes patients in primary care setting in Southeastern Brazil
Heverton Alves Peres, Leonardo Régis Leira Pereira, Edson Zangiacomine Martinez, Carlos Manuel Viana, Maria Cristina Foss de Freitas
Primary Care Diabetes.2020; 14(1): 85. CrossRef - Predictors of poor adherence to antidiabetic therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes: a cross-sectional study insight from Ethiopia
Gebre Teklemariam Demoz, Shishay Wahdey, Degena Bahrey, Halefom Kahsay, Gebremariam Woldu, Yirga Legesse Niriayo, Andrew Collier
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of medication storage with diabetes control: A cross-sectional study from Saudi Arabia
Ali F. Altebainawi, Mubarak N. Alrashidi, Moaath K. Aljbreen, Muhammad Majid Aziz, Abdullah A. Alhifany, Mohamad Aljofan, Thamir M. Alshammari
Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal.2020; 28(4): 452. CrossRef - Facteurs associés à la non-observance thérapeutique chez les diabétiques de type 2 : première enquête algérienne
M.Y. Achouri, M. Mammeri, Y. Sehanine, M.A. Selka, W.I. Ghomari, A. Lahmer, M. Hadj Habib
Annales Pharmaceutiques Françaises.2019; 77(6): 506. CrossRef - Heart failure is associated with non-adherence to pharmacotherapy in elderly with type 2 diabetes mellitus in public health system Brazilians
Heverton Alves Peres, Leonardo Régis Leira Pereira, Edson Zangiacomini Martinez, Carlos Manuel Viana, Maria Cristina Foss-Freitas
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2019; 13(2): 939. CrossRef - Medication Adherence and its Predictors in Type 2 Diabetic Patients Referring to Urban Primary Health Care Centers in Kerman City, Southeastern Iran
Lila Benrazavy, Ali Khalooei
Shiraz E-Medical Journal.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Adherence to Bisphosphonates among People Admitted to an Orthopaedic and Geriatric Ward at a University Hospital in Sweden
Linnea Abramsson, Maria Gustafsson
Pharmacy.2018; 6(1): 20. CrossRef - Evaluation of factors for therapeutic adherence in diabetic patients
G. Belhabib, M. Lahyani, A. Mhiri, O. Gloulou, J. Sahli, N. Chouchane
Le Pharmacien Hospitalier et Clinicien.2018; 53(2): 159. CrossRef - Évaluation des facteurs conditionnant l’observance thérapeutique chez le patient diabétique
G. Belhabib, M. Lahyani, A. Mhiri, O. Gloulou, J. Sahli, N. Chouchane
Le Pharmacien Hospitalier et Clinicien.2018; 53(2): 87. CrossRef - Factors associated with antidiabetic medication non-adherence in patients with incident comorbid depression
Carlotta Lunghi, Arsène Zongo, Jocelyne Moisan, Jean-Pierre Grégoire, Line Guénette
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2017; 31(7): 1200. CrossRef - Psychosocial factors associated with adherence to non-insulin antidiabetes treatments
Line Guénette, Marie-Claude Breton, Laurence Guillaumie, Sophie Lauzier, Jean-Pierre Grégoire, Jocelyne Moisan
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2016; 30(2): 335. CrossRef - Effects of pharmacist-led patient education on diabetes-related knowledge and medication adherence: A home-based study
Ee Pin Chow, Mohamed Azmi Hassali, Fahad Saleem, Hisham Aljadhey
Health Education Journal.2016; 75(4): 421. CrossRef - Adherence to diabetes medication: a systematic review
I. Krass, P. Schieback, T. Dhippayom
Diabetic Medicine.2015; 32(6): 725. CrossRef - Study on prevalence and factors influencing patient’s adherence to anti-diabetic medications in Urban Pondicherry
P. Stalin, Zile Singh, Anil J. Purty, Yogesh Sharma, Sherin Billy Abraham
International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries.2015; 35(S2): 128. CrossRef - Adherence to anti diabetic medication among patients with diabetes in eastern Uganda; a cross sectional study
James Bagonza, Elizeus Rutebemberwa, William Bazeyo
BMC Health Services Research.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - The role of social support on the relationship of depressive symptoms to medication adherence and self‐care activities in adults with type 2 diabetes
Chun‐Ja Kim, Elizabeth A. Schlenk, Dae Jung Kim, Moonsun Kim, Judith A. Erlen, Se‐Eun Kim
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2015; 71(9): 2164. CrossRef - Adesão ao tratamento do diabetes mellitus e variáveis sociodemográficas, clinicas e de controle metabólico
Clarissa Cordeiro Alves Arrelias, Heloisa Turcatto Gimenes Faria, Carla Regina de Souza Teixeira, Manoel Antônio dos Santos, Maria Lucia Zanetti
Acta Paulista de Enfermagem.2015; 28(4): 315. CrossRef - The Effectiveness of Short Term Mobile Phone Text Reminders in Improving Compliance among Hypertensive Patients
Jung Ah Lee, Woo Sang Kim, Moon Jung Bae, Young-Sik Kim, Han Jin Oh, Sang Yeoup Lee, Chul-Min Kim, Dong Hyeok Shin, Seong-Ho Han, Kyung-Hwan Cho
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2014; 14(1): 1. CrossRef - Role of depressive symptoms and self‐efficacy of medication adherence in Korean patients after successful percutaneous coronary intervention
Youn‐Jung Son, Sun‐Hee Kim, Jin‐Hee Park
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2014; 20(6): 564. CrossRef - Non-adherence and Associated Factors among Type 2 Diabetic Patients at Jimma University Specialized Hospital, Southwest Ethiopia
Gebrehiwot Teklay, Jemal Hussien, Dawit Tesfaye
Journal of Medical Sciences.2013; 13(7): 578. CrossRef - Conocimientos, percepciones y actitudes que intervienen en la adherencia al tratamiento en pacientes ancianos polimedicados desde una perspectiva cualitativa
E. Crespillo-García, F. Rivas-Ruiz, E. Contreras Fernández, P. Castellano Muñoz, G. Suárez Alemán, E. Pérez-Trueba
Revista de Calidad Asistencial.2013; 28(1): 56. CrossRef - Positive Psychological Characteristics in Diabetes: A Review
Christopher M. Celano, Eleanor E. Beale, Shannon V. Moore, Deborah J. Wexler, Jeff C. Huffman
Current Diabetes Reports.2013; 13(6): 917. CrossRef - The Effect of a Clinic Based Incentive Program on Medication Adherence among Patients with Hypertension or Diabetes Mellitus in Incheon
Won Cheong, Jun Yim, Dae-Kyu Oh, Jeong-Soo Im, Kwang Pil Ko, Ie Byung Park
Health Policy and Management.2013; 23(4): 427. CrossRef - Difficulty adhering to antidiabetic treatment: Factors associated with persistence and compliance
L. Guénette, J. Moisan, M.-C. Breton, C. Sirois, J.-P. Grégoire
Diabetes & Metabolism.2013; 39(3): 250. CrossRef - Impact of Cognitive Function and Self-efficacy on Medication Adherence of Elderly Patients with Chronic Disease
Kyung-Hee Ryu, Youn-Jung Son
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2013; 15(3): 107. CrossRef - Prevalence and correlates of self-reported medication non-adherence among older adults with coronary heart disease, diabetes mellitus, and/or hypertension
Zachary A. Marcum, Yan Zheng, Subashan Perera, Elsa Strotmeyer, Anne B. Newman, Eleanor M. Simonsick, Ronald I. Shorr, Douglas C. Bauer, Julie M. Donohue, Joseph T. Hanlon
Research in Social and Administrative Pharmacy.2013; 9(6): 817. CrossRef - Medication Adherence in Type 2 Diabetes: The ENTRED Study 2007, a French Population-Based Study
Michel Tiv, Jean-François Viel, Frédéric Mauny, Eveline Eschwège, Alain Weill, Cécile Fournier, Anne Fagot-Campagna, Alfred Penfornis, German Malaga
PLoS ONE.2012; 7(3): e32412. CrossRef - Construction of Explanatory Model for Medication Adherence in Older People with Chronic disease
Shin Hong Min, Jong Im Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2012; 19(4): 463. CrossRef - The Effects of Tele-care Case Management Services for Medical Aid Beneficiaries
Yang Heui Ahn, Eui Sook Kim, Il Sun Ko
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2010; 21(3): 351. CrossRef
- Medication use problems among older adults at a primary care: A narrative of literature review

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





